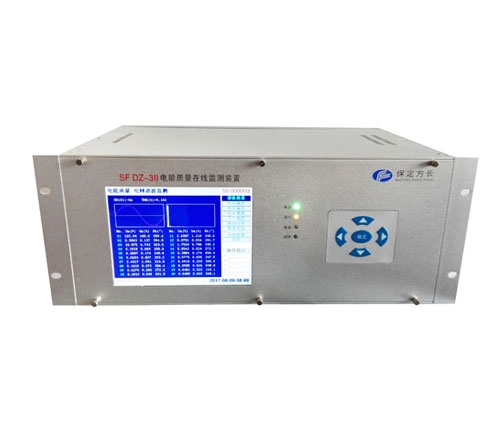
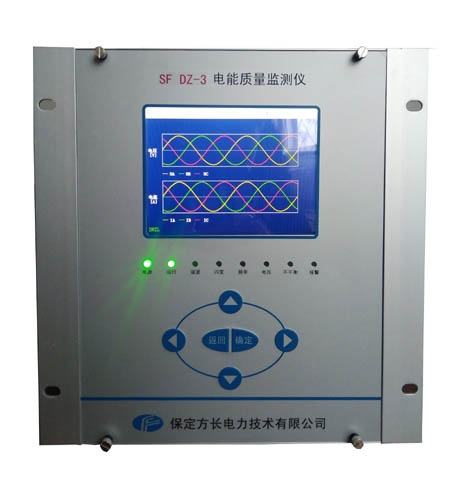
1. Changes in the composition of power load
There are a large number of nonlinear loads in the power system: large-scale power electronic application devices (energy-saving devices, frequency conversion devices, etc.), high-power power traction equipment, DC output devices, electrochemical industrial equipment (rectification of chemical and metallurgical enterprises), electrified railways, steelmaking electric arc furnaces (AC and DC), rolling mills, elevators, calcium carbide machines, induction heating furnaces, and other nonlinear loads.
2. Large amount of harmonics injected into the power grid
New types of power equipment containing nonlinear and impulsive loads inevitably generate non sinusoidal waveform currents while achieving power control and processing, injecting harmonic currents into the power grid, causing serious distortion of the voltage waveform at the common connection point (PCC). The load fluctuation and impact characteristics lead to various power quality disturbances such as voltage fluctuations and instantaneous pulses.
3. Automatic protection and normal operation of power equipment and devices
The start-up and shutdown of large power equipment, as well as the tripping and reclosing of automatic switches, have an impact on power quality, causing temporary reduction in rated voltage, voltage fluctuations and flickers, and also affecting power quality.
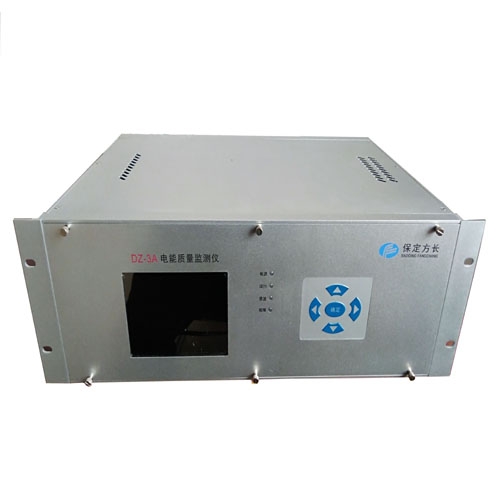

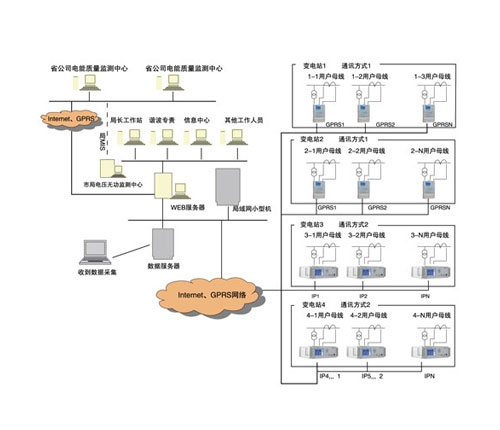
Power quality monitoringdeviceThe important indicators include voltage quality, current quality, power supply quality, power consumption quality, etc. Among them, power supply quality, electricity consumption quality, and other indicators collectively reflect the quality of electricity produced and transmitted by the power system, and can be used to manage electricity based on these indicators.
Current quality refers to the deviation between the actual voltage and the ideal voltage, reflecting whether the power supply enterprise provides qualified electricity to users. The deviation here should be generalized, including amplitude, waveform, and phase. This definition includes most power quality issues, but does not include power quality issues caused by frequency, nor does it include the impact and pollution of electrical equipment on the power quality of the grid.
The current quality reflects the changes in current that are closely related to the voltage quality. In addition to the requirement of constant frequency and sinusoidal waveform for AC power sources, power users also require the current waveform to be in phase with the voltage to ensure high power factor operation. This definition helps to improve the quality of power grid and reduce line losses, but cannot summarize most quality problems caused by voltage reasons.
![]() National ordering hotline:fifteen billion eight hundred and three million one hundred and twenty-five thousand five hundred and sixty-five
National ordering hotline:fifteen billion eight hundred and three million one hundred and twenty-five thousand five hundred and sixty-five